- magnetron
- A diode-type vacuum tube in which the flow of electrons is controlled by a magnetic field external to the tube. A magnetron is used to produce high-power electromagnetic energy in the frequency range of 1 to 40 GHz. Magnetron tubes find application in radars. Most magnetrons have a central cathode and a surrounding plate. This plate is usually divided into two or more sections by radial barriers called cavities. The RF (radio frequency) output is taken from a wave-guide opening into the anode. The cathode is connected to the negative terminal of a high-voltage source, while the anode is connected to the positive terminal. The electrons start flowing from the cathode to the anode. Application of the magnetic field in a longitudinal direction causes the electrons to travel outward in a spiral instead of along a straight path. The electrons travel in bunches because of the interaction between the electric and magnetic fields, and this results in oscillations, with the frequency being somewhat stabilized by the cavities. Magnetrons can produce continuous power outputs of more than 1 kW at a frequency of 1 GHz. The output drops as the frequency increases. For example, at 10 GHz, a magnetron can produce about 10 to 20 watts of continuous radio frequency output. For pulse modulation, the peak-power values are much higher.
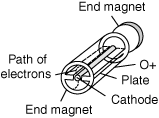 The magnetron produces oscillation because of the influence of a magnetic field on motion of electrons.
The magnetron produces oscillation because of the influence of a magnetic field on motion of electrons.
Aviation dictionary. 2014.
